

Technology continues to reshape the freight forwarding industry globally, and Nigerian businesses are increasingly adopting digital solutions to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance customer experience. As 2026 approaches, understanding the key technology trends in freight forwarding is essential for importers, exporters, and logistics companies looking to remain competitive in Nigeria’s rapidly evolving market.
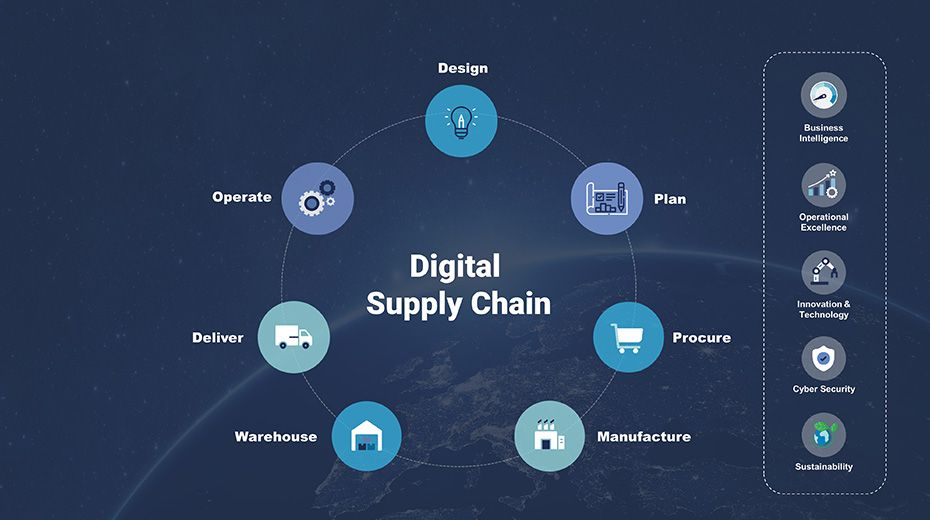
1. End-to-End Digital Documentation
Traditionally, freight forwarding relied heavily on paper-based documentation, which often led to delays and human errors. In 2026, Nigerian forwarders are increasingly adopting digital platforms to handle:
- Form M and PAAR submissions
- Electronic Bills of Lading (eBL)
- Single Goods Declarations (SGD)
- Shipping invoices and packing lists
This digitization reduces manual processing time, improves accuracy, and minimizes delays at Nigerian ports.
2. Real-Time Cargo Tracking
GPS-enabled tracking systems now allow importers and exporters to monitor shipments at every stage:
- Vessel or aircraft departure and arrival
- Transit through ports or warehouses
- Last-mile delivery
Real-time visibility not only improves transparency but also helps businesses plan inventory and operations more effectively, reducing storage costs and lost shipments.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Logistics
AI is transforming freight forwarding by enabling predictive analytics and automated decision-making. Applications include:
- Optimizing shipping routes to reduce time and fuel costs
- Predicting freight rate fluctuations for budget planning
- Identifying high-risk shipments that may trigger customs inspections
- Automated error detection in documentation
AI adoption improves accuracy, speeds up cargo clearance, and reduces operational inefficiencies.
4. Warehouse Automation
Advanced warehousing solutions are becoming more common in Nigeria:
- Automated sorting and inventory management
- Robotics for loading and unloading
- Digital scanning for verification of goods
- AI-powered demand forecasting
These systems improve handling speed, reduce human error, and enhance customer satisfaction.
5. Blockchain for Secure Documentation
Blockchain technology is being adopted to ensure secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transaction records. Benefits include:
- Verification of cargo origin and ownership
- Reduced fraud and disputes
- Faster processing of customs documentation
Blockchain enhances trust between freight forwarders, importers, and regulatory agencies.
6. Digital Customer Portals
Forwarders now offer online portals where clients can:
- Book shipments and manage orders
- Upload documents securely
- Track cargo status in real-time
- Pay invoices and download receipts
Customer portals enhance self-service capabilities, reducing communication delays and increasing operational efficiency.
7. Cybersecurity Measures
As the industry becomes more digital, cybersecurity is crucial. Nigerian forwarders must protect:
- Shipment data
- Client financial information
- Internal logistics systems
Investments in secure payment systems, encrypted platforms, and staff cybersecurity training are becoming standard practice.
Conclusion
Technology is no longer optional in freight forwarding—it is a competitive necessity. Nigerian businesses in 2026 that adopt digital documentation, AI-driven tracking, warehouse automation, and secure blockchain solutions will enjoy faster clearance, lower operational costs, and better customer service. Freight forwarders who embrace these innovations will dominate the market, while importers and exporters who align with tech-savvy partners will gain a significant edge in efficiency and profitability.